How to develop the sustainable hospital of tomorrow? Hospitals consume a lot of energy, produce a lot of medical waste and sometimes use harmful chemicals. These practices have a significant environmental impact and require sustainable solutions.
I. A brief overview of ecology and sustainable development in hospitals

What is the current consumption of French hospitals?
Today, French hospitals consume an average of 320 kWh per m² per year(ADEME). Statistics show that hospitals account for a significant proportion of public sector energy consumption. According toADEME, their energy consumption accounts for 11% of the entire tertiary sector in France. And according to the Agence de la Transition Ecologique, this energy consumption is mainly due to due to heating and air conditioning, which account for almost 50-60% of the bill.
How is hospital waste management organized ?
Hospitals produce different types of waste: medical, plastic and organic. Current management methods include incineration, recycling and specific treatment of hazardous medical waste. Nantes University Hospital, for example, is connected to the urban heating network, 85% of which is supplied by waste incineration. The Covid 19 crisis didn’t help matters, however, drastically increasing the use of single-use equipment, thus multiplying waste production.
Use of chemical and pharmaceutical products in hospitals
The chemicals used in hospitals have a negative environmental impact. Chemical hazards: irritant, corrosive, reactive with water and air, explosive, oxidizing or flammable. Toxic vapors that can be inhaled or cause irritation. Damage to materials, equipment and structures. Discharges into the sewage system contaminate the environment. Current management practices aim to reduce their use and find less harmful alternatives.
II. Green initiatives to improve the hospital’s carbon footprint

A hospital that consumes less
Hospitals are installing more efficient heating, ventilation and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems. They also use renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. Many initiatives aim to reduce the carbon footprint of healthcare facilities.
In a hospital complex like Lyon‘s, the heating and electricity bill can quickly reach 15 million euros, or 1% of the budget. We have stepped up our efforts to reduce energy costs as much as possible. Working on supply and distribution, a compartmental metering and sub-metering system was deployed to identify anomalies, particularly leaks. In 15 years, water consumption has been divided by three, dropping from 2 millionm3 a year to 700,000m3 today.
The Cornouaille Hospital, for example, is one of the leading hospitals in France in this area, having embarked on a Sustainable and Eco-responsible Hospital initiative aimed at reducing the environmental impact of its activities.
More sustainable waste management
Recycling and composting programs are in place to manage waste sustainably. Innovations, such as the treatment of medical waste using advanced technologies, are underway. Reducing the use of single-use plastics is also a priority. The figures are astronomical. Every year, humanity produces over 450 million tonnes of plastic, a third of which is used only once. Of the 8,300 billion tonnes produced since 1950, 30% are still in use, 10% have been incinerated and 60% have ended up as waste (30% landfilled, 30% discharged into the environment)..
Use of environmentally-friendly products
Hospitals are replacing hazardous chemicals with environmentally-friendly alternatives. They are also working to reduce the use of pharmaceutical products with a high environmental impact.
The example of GRØNNKÖPINGKIÐ UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL
The GRØNNKÖPINGKIÐ University Hospital, often referred to as “the world’s greenest hospital”, is a fictitious hospital that exemplifies ecology and sustainable development. This imaginary digital hospital has been designed to showcase Nordic solutions at the forefront of environmentally-friendly healthcare services. It uses innovative green technologies and sustainable practices. This hospital is reducing its carbon footprint thanks to renewable energies and energy efficiency. It promotes the sustainable management of resources such as water and waste, and takes a global approach to environmental health.

III. Innovations for sustainable hospital development
Sustainable and environmentally-friendly technologies: numerous use cases
Hospitals use advanced technologies to reduce energy consumption.
Optimizing waste management
For example, innovations in waste treatment and management, such as Sterilwave based on microwave technology. Thanks to the grinding and disinfection stages, it enables bacterial inactivation of medical waste in 30 minutes, with the operator needing only 5 to 10 minutes.
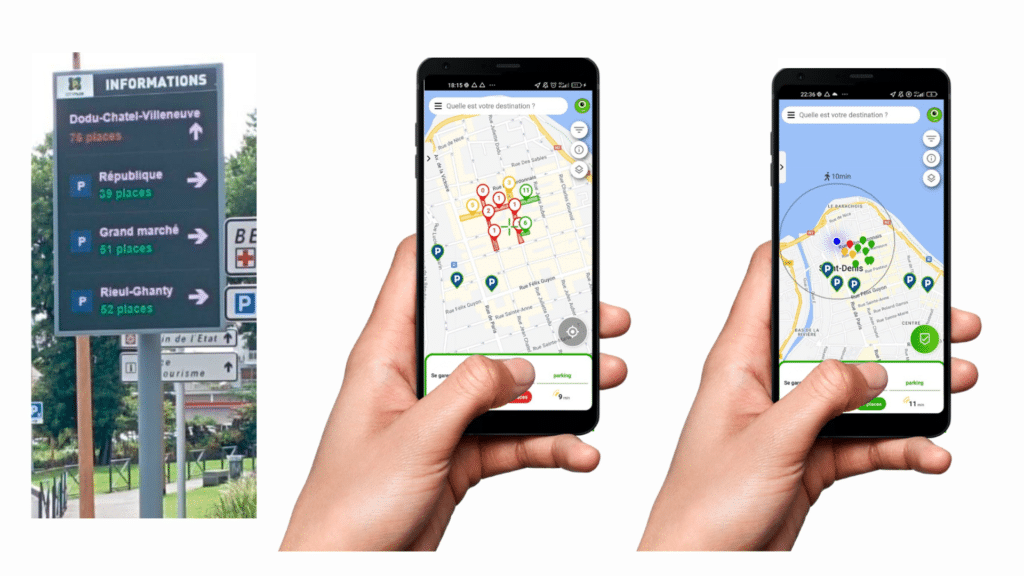
Smart parking and intelligent parking for a sustainable hospital
On the other hand, deploying an intelligent parking display system optimizes the use of parking spaces. In this way, users are directed directly to the available spaces. Information is displayed via a mobile application, dynamic panels for the general public, and a control panel for decision-makers. In this way, the time spent looking for a parking space is reduced, traffic in the parking lot is reduced and C02 emissions are also reduced. Cocoparks deploys a complete, simple and effective solution to combat these effects.
Infrastructure construction and renovation
Green hospital building design uses sustainable, environmentally-friendly materials. Hospitals also improve the energy efficiency of existing buildings, contributing to a reduced carbon footprint. Nantes University Hospital, for example, has installed 5 geothermal wells to enhance its energy independence, as well as 2,500 m² of photovoltaic panels.
Organizational sustainability practices and sustainable hospitals
Staff training and awareness-raising initiatives are essential. Working with environmentally-friendly suppliers reinforces our commitment to sustainable development. Internal policies encourage sustainable practices.
That’s what the Chartreuse hospital has done with its charter of commitment to a responsible, sustainable hospital. The“Plan Health Faire” helps you understand the key issues of sustainable development as applied to healthcare. It gives you the tools you need to take action within your facility, rethink your professional practice and contribute to controlling environmental, climatic, societal and health risks.


